UV disinfection is a treatment technology used for
the production of pure water! UV disinfection works by emitting radiation via a
light wave and is particularly effective against micro-organisms and pathogens
such as bacteria, viruses or protozoa. Learn more about the capital and
operational costs, the functioning, the strengths and weaknesses and even the
different uses of UV disinfection systems.
Il est à noter que nous abordons le sujet d’un point de vue industriel, mais que le fonctionnement d’un système résidentiel est très semblable. De plus, les prix donnés dans l’article sont des estimations et peuvent varier de façon importante en fonction des différentes situations.
What is UV disinfection (irradiation)?
Les traitements UV sont un type de désinfection permettant la désactivation de certains organismes pouvant se retrouver dans l’eau. Cette désinfection fait généralement partie de l’étape de polissage de l’eau et elle ne peut pas être utilisée comme traitement primaire puisqu’elle serait inefficace contre une eau trop chargée.
This type of disinfection works on the principle of irradiation. The irradiation is done by using a mercury lamp which, via an electromagnetic transfer, sends energy that will attack the genetic material (DNA) of the organisms present in the water.
In other words, when activated, UV lamps emit waves of 185nm or 254nm in length that will attack the particles in the water. In comparison, UV waves are much shorter than infrared waves, which generally measure 780nm to 1mm.
Pour détruite les contaminants, l’ultraviolet est absorbé par les bases d'ADN des micro-organismes et y provoquera des modifications au niveau des liens chimiques. Ces changement interfèrent avec la transcription et la réplication de l'ADN, désactivant ainsi la capacité de multiplication de la cellule. La radiation UV est donc un agent mesurable qui endommage directement l'ADN.
Pour fonctionner, la lampe UV émettra ses ondes à l’intérieur d’un boîtier où l’eau traitée passera. Les ondes émises sont sous forme de lumières monochromatiques qui peuvent changer en fonction du type de lampe utilisée. L’efficacité du traitement UV est intimement liée aux paramètres de l’eau, à l’intensité des lampes et au temps d’exposition. Les paramètres de l’eau affectent l’efficacité du traitement UV puisque la présence de particules ou tout autre type d’obstructions affectent grandement les ondes émises puisqu’elles peuvent être facilement bloquées. C’est principalement pour cette raison que l’irradiation UV ne peut être utilisée comme traitement primaire.
Uses of UV disinfection
Très répandues dans bien des secteurs comme le domaine pharmaceutique, l’alimentaire et la production d’eau ultra pure, la désinfection UV est très efficace contre les bactéries, les virus, les spores, les kystes et tous les autres types de micro-organisme. L'UV peut également être utilisée pour éliminer l'ozone résiduel suite à une ozonation ou en combinaison avec l'ozone pour un traitement d'oxydation avancé.
On the other hand, it is useless to install a UV disinfection system alone if your water is heavily contaminated with organic compounds or suspended solids. A primary treatment would then be necessary before the UV polishing. In addition, it is important to remember that this type of disinfection will not affect the color of the water and that even though the micro-organisms will be deactivated by the UV irradiation, their bodies will remain in the water and create sediment. For the production of ultra pure water, these bodies must be removed by downstream filtration.
Strengths and Weaknesses of UV Disinfection
Pour commencer, les systèmes de désinfection UV présentent l’avantage d’être peu coûteux au niveau opérationnels. En effet, les lampes durent en moyenne de 9 à 12 mois et lorsqu’elles sont à changer, elles coûtent environ 100 à 200$ chacune. Donc, le coût de remplacement des lampes varie en fonction du système possédé et du nombre de lampes présentes à l’intérieur de l'équipement. Ensuite, le manchon de protection ou Sleeve pour la lampe doit être changé au 12-24mois puisqu’il s’abîme avec le temps et finit par affecter l’efficacité des ondes UV. Comme les lampes UV, les sleeves coûtent entre 100 et 200$ chacune. Outre ces coûts, il faut prendre en compte la demande énergétique pour un traitement en continu.
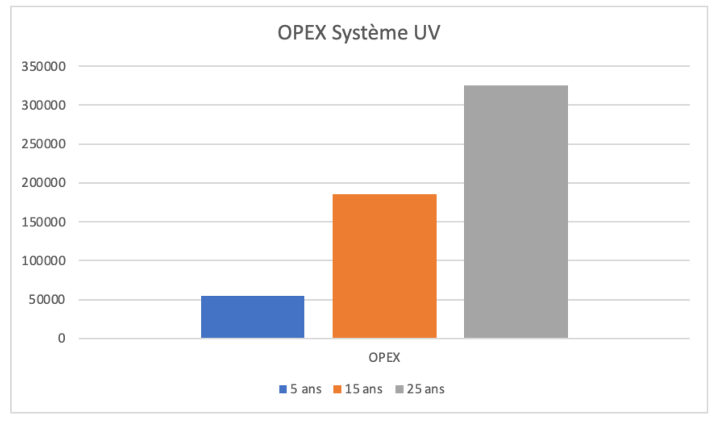
- The estimated costs are based on a system providing approximately 500 GPM of treatment and we have included the following costs in the estimate: energy, lamps, labor.
- It is important to note that these are only estimates and that these costs can vary greatly depending on the system, demand and situation.
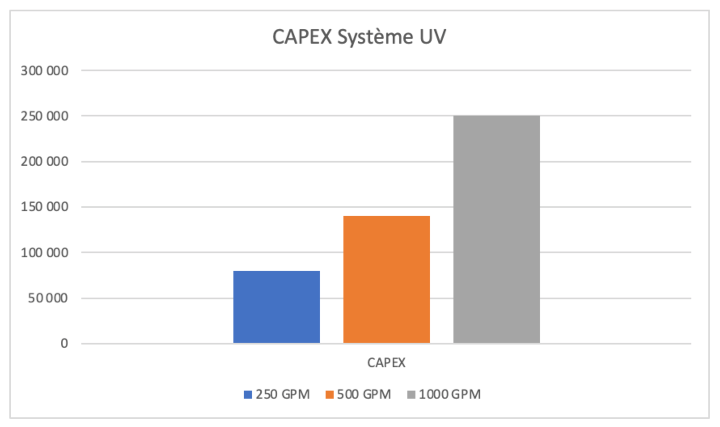
In terms of the CAPEX of a UV system, again, the costs are relatively low. When purchasing a system, the factors to consider are generally the purchase of the reaction chamber, which is where the disinfectçakes place. Then, the electronic equipment that allows the lamps to light up: ballast, intensity sensor, controller, etc. And finally, the installation and activation costs.
As mentioned above, the UV treatment is continuous, which means that the disinfection never stops and that no decrease in production is perceived when there is a treatment. Moreover, contrary to what one may believe, UV irradiation is a physical process and not a chemical one. This means that no transportation, storage or handling of chemicals is required.
Although UV disinfection systems have many advantages, it is important to remember that they are not suitable for use as a primary treatment. In addition, there may be times when it is not effective or when standards require the use of some chemical. In these cases, UV irradiation can be used to remove the residues of the chemicals used upstream. Several factors can make that a UV disinfection is not sufficient, we can think of the photoreactivation which is a mechanism of repair of the DNA allowing certain contaminants like the prokaryotes or the eukaryotes to recover their capacity of reproduction.
Finally, it should be noted that handling UV lamps is a challenge as they cannot be stored for too long and should not be touched with bare hands. As mentioned above, UV waves are easily blocked by any contaminants. Touching the sleeve or the UV lamp will leave a fingerprint on it and affect the effectiveness of the irradiation.
A good solution, according to your needs
As you have seen, UV disinfection is an interesting option in many ways and has varying capabilities depending on its use. It is important to understand that this physical water treatment process is primarily used in the production of high-purity water. It is not a necessary treatment for all industrial applications.
On this note, we hope that we have answered your questions about this type of disinfection. If you would like to learn more about other types of disinfection used in the pharmaceutical industry, I invite you to visit this article: disinfection technique for a pharmaceutical water purification system.
In the meantime, if you have any questions or comments, we will be happy to answer them.